Freezing thickness of a brick wall. External load-bearing structures made of brick: features, calculations, design. Internal and external load-bearing structures
– this is already a priori a symbol of reliability and safety. However, for this to happen in reality, you need to approach it with knowledge of the matter and the technological aspects of the entire process. One of the most significant points is the calculation of a brick wall.
The secret of popularity
Why has this building material remained relevant for a century? There are a number of explanations for this:
- Structures made from it are distinguished by high strength.
- Affordable price.
- Versatility (suitable for the construction of cottages and multi-storey buildings).
- Surfaces made of this material have high and excellent sound insulation.
All these qualities will manifest themselves provided that the work is carried out correctly. And here the thickness of the surface itself will play a primary role.
The relationship between thickness and masonry
This important indicator will affect the operational characteristics of the facility. Among them are reliability and its consumer capabilities. If the work is not done according to GOST recommendations, then living in such a room may not be very comfortable at all.
It is best that the masonry is done in several layers. This guarantees subsequent high performance. You can determine what exactly it should be if you refer to specialized regulatory requirements. Most often they are reflected in the relevant documentation.
Current factors
When calculating the thickness brick wall, you should pay attention to several important points.
Among them are:
Under these conditions, all the very important components can be seen to form one successful puzzle. It will ultimately provide the building with the necessary thermal insulation and elegant appearance.
What should the thickness be?
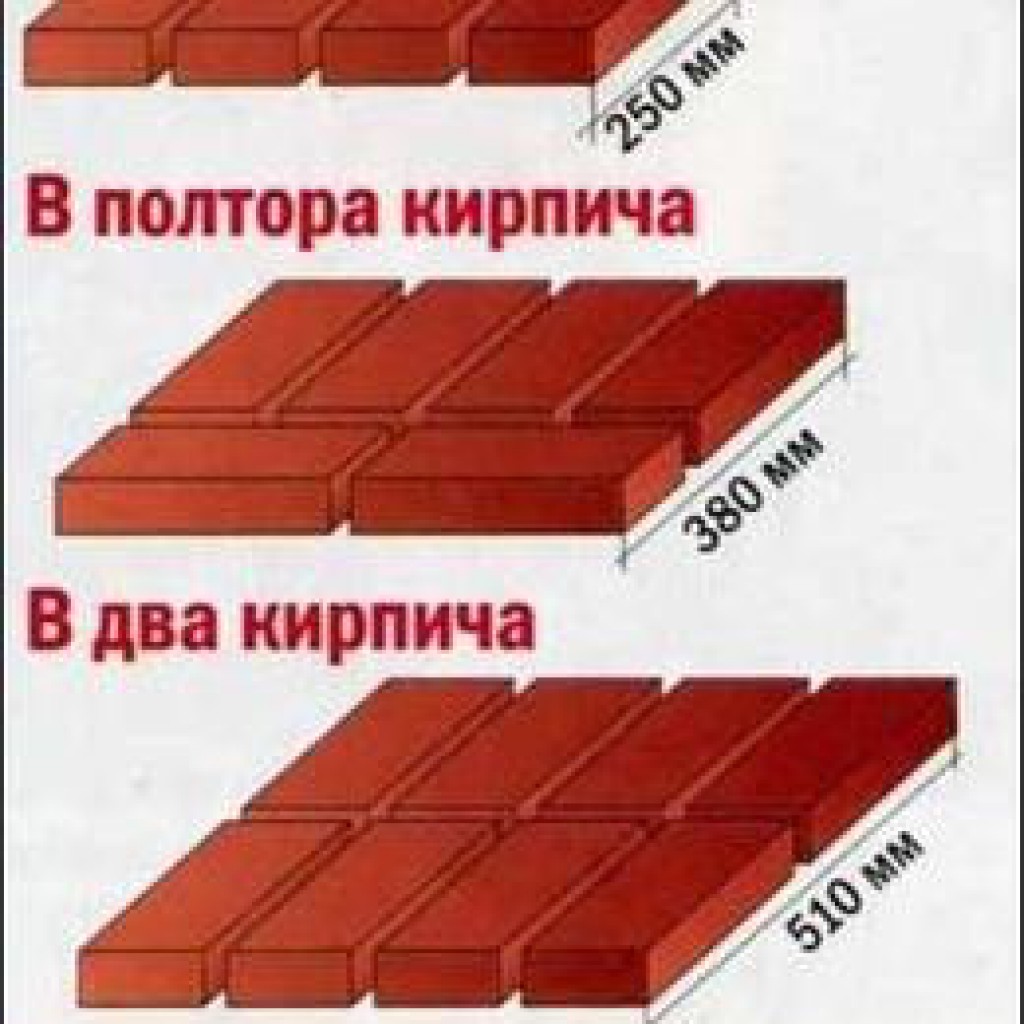
Such an important parameter as thickness will depend on how many pieces of the specified material are planned for its laying. In total, this can vary from 12 to 64 cm. The following possibilities are distinguished:
- half a brick (12 cm);
- in one (25 cm);
- one and a half (38 cm);
- in two pieces (51 cm);
- two and a half (64 cm).
If we talk about the climatic features of the area, then for a temperate climate it is recommended to place from 2 to 2.5 elements. In addition, upon completion of construction, it would be best to additionally insulate it (for example, using mineral wool).
Some experts emphasize that there is a necessary margin of safety. It can be 38 cm.
Features of the construction of load-bearing structures

Such walls are designed to form a rigid frame inside a building. The strength and reliability of the structure will depend on them. They bear the load not only on their own weight, but also take into account all the partitions, ceilings and roofs included in the building. That is why very important requirements are placed on them - and especially on the material from which they will be built. Built taking into account all recommendations, they will retain all the necessary heat-saving properties.
When constructing external walls that will have a load-bearing function, their thickness must be at least 51 cm. According to the above requirements, this is a two-brick masonry. The maximum threshold used is also indicated - 64 cm (2.5 pieces).
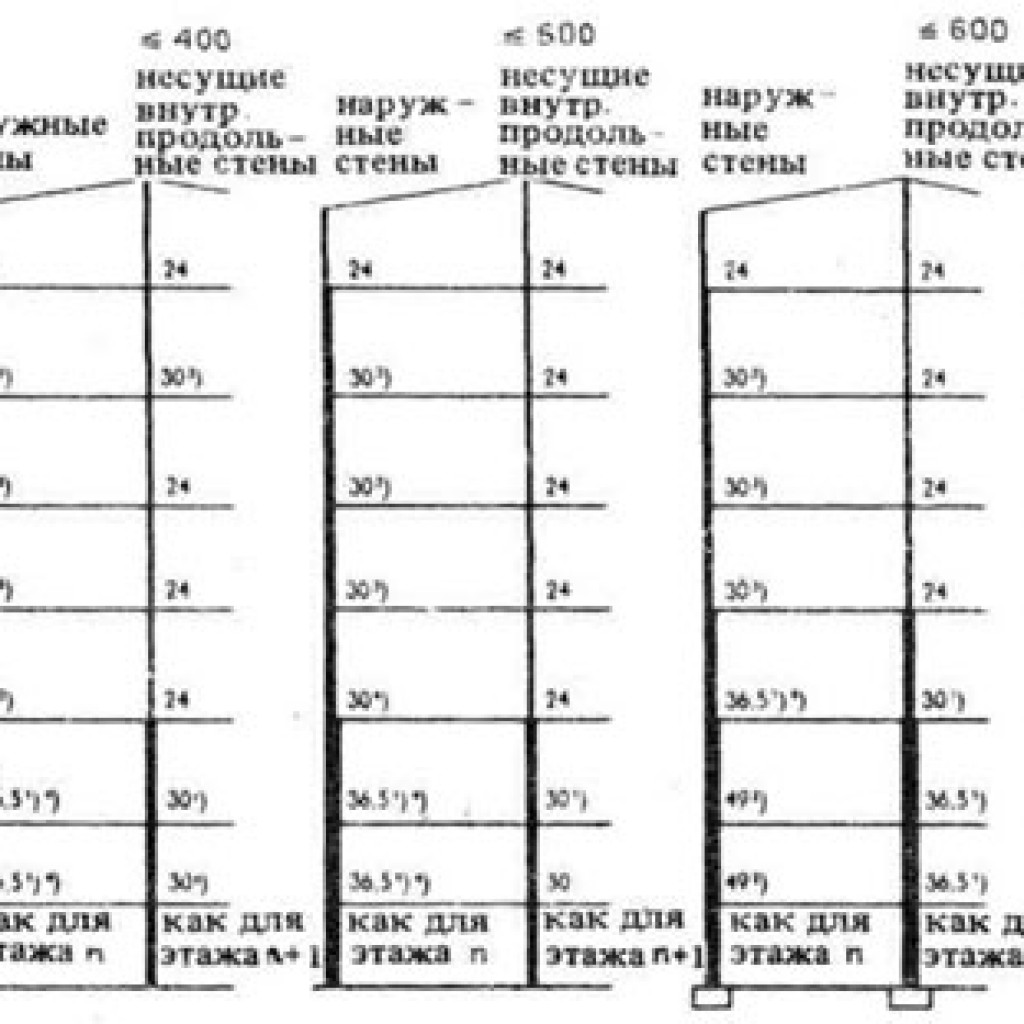
In the event that multi-storey construction is planned, the width of the load-bearing brick wall will be a uniform decrease as the height of the building increases: if at the level of the first floor it is 2.5 pieces, then from the fifth floor - only two. Will this affect thermal conductivity? No, this increase will be compensated by the fact that a large layer of thermal insulation will be used.
For low-rise construction, it is also important to comply with the necessary requirements: the load-bearing wall should not be less than two units thick. However, reasonable savings are also possible: for its purposes, it is possible to reduce this figure to one and a half sizes.
Don't forget to look inside the room. Here it is also very important to follow certain recommendations
:
- for load-bearing walls it is recommended to use a thickness of at least one brick;
- if we are talking about a partition (that is, simple zoning of space), then masonry half the size of the accepted unit is allowed.
In the latter case, there is a risk that the wall will not be rigid enough - in this case it will need to be leveled and reinforced with ordinary wire. It must be placed in mortar joints. You can also save money in this case by replacing the material with foam or aerated concrete.
How to perform the correct calculation
There is a formula that will help you understand how thick such a wall should be. It is performed as R = S/k thermal conductivity:
- S (material thickness, measured in meters);
- R (thermal resistance is different for each region).
Any presented material has its own thermal conductivity coefficient. For example, in the case of a single one it will be 0.58 W/m °C. This indicator is established by state standards. read the article at the link.
Individual element thickness

When calculating the thickness of a brick wall, you also need to take into account how thick its individual element will be. In modern construction it is common to use the following types:
- single;
- one and a half;
- double.
The most common unit of brick will have the following dimensions - 25 x 1.2 x 6.5 cm. These dimensions have remained unchanged since the first half of the last century, when they were fixed in the relevant documentation. For a one and a half copy, the size will be 25x12x8.8 cm. It would be even better to use a double version for external walls. Its dimensions are 2.5 cm x 12 cm x 13.8 cm.
Thermal conductivity as an important aspect of choosing a building material
Of great importance in the construction of any building is the ability of the walls to conduct heat. In this regard, brick is not the best best results. In this parameter it is inferior to wood.
What is this indicator equal to? For a solid one, it is usually about 0.6 - 0.7 W/m°C. It can be reduced by using a hollow version (even three times). But you need to immediately take into account the fact that in this case such a material will conduct heat much worse and at the same time a decrease in its strength is noted. Therefore, this type is best used in individual cases.
But during the construction of the foundation, plinth and basement, there is a taboo on the use of the hollow type. And under no circumstances should it be allowed to come into contact with water.
How to save on masonry

The thickness of any brick wall- this is the parameter that is determined during the design process of the house. Being selected according to all the rules, it will help save both time and money, ensure reliability and durability in maintenance, and play a positive role in the wear resistance of any structure. However, such an event is often costly for the budget. There are some options to help deal with this problem:
- In low-rise construction, it is quite possible to use lightweight masonry. It is made like a well: that is, two different walls will be built at a short distance from each other (0.5 bricks are used in each).
- The resulting air gap will be a good heat insulator. This will happen due to the fact that the air does not conduct heat very well.
- Additionally, you can “fill” such a cavity with expanded clay, foam concrete and similar materials.
- In order for the structure to be more rigid, it will be necessary to connect the walls using diaphragms. This decision will make the construction of such a building more economically profitable.
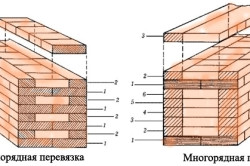
Features of masonry of various thicknesses

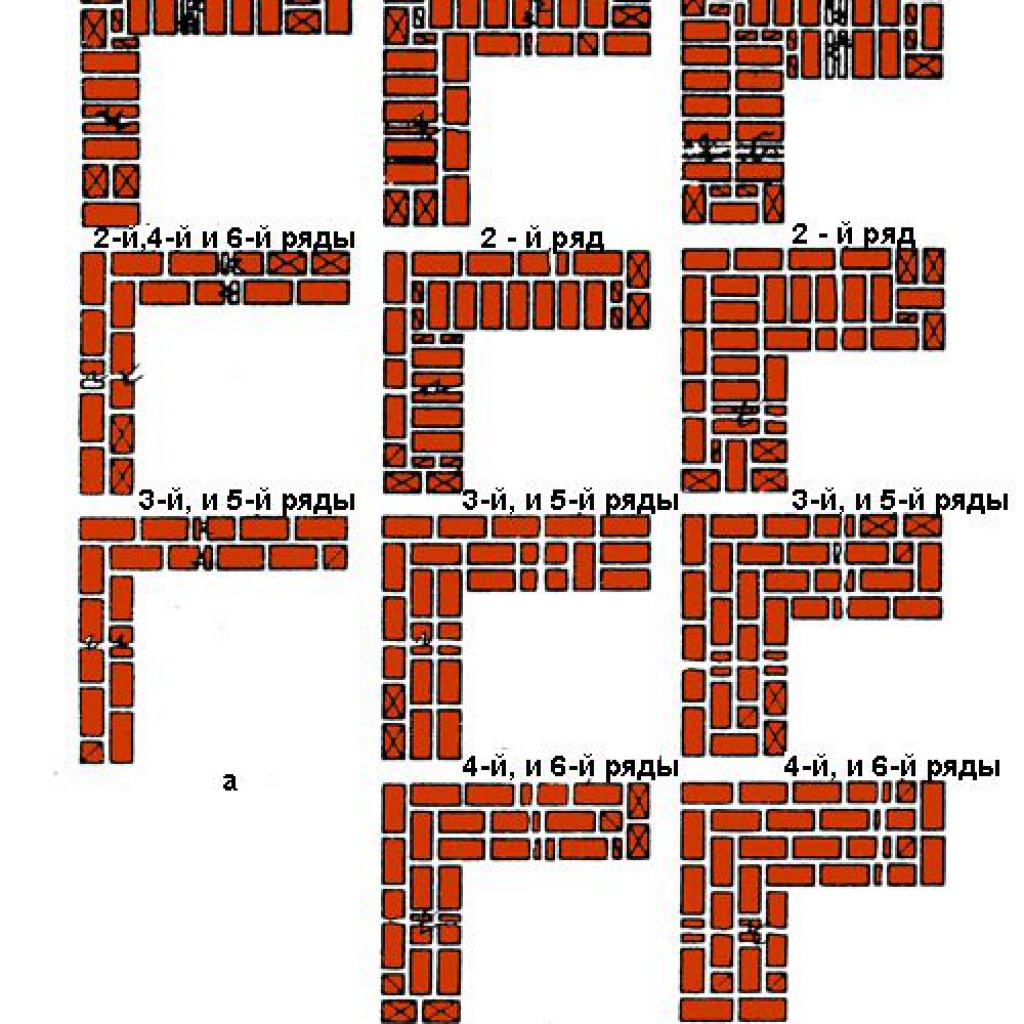
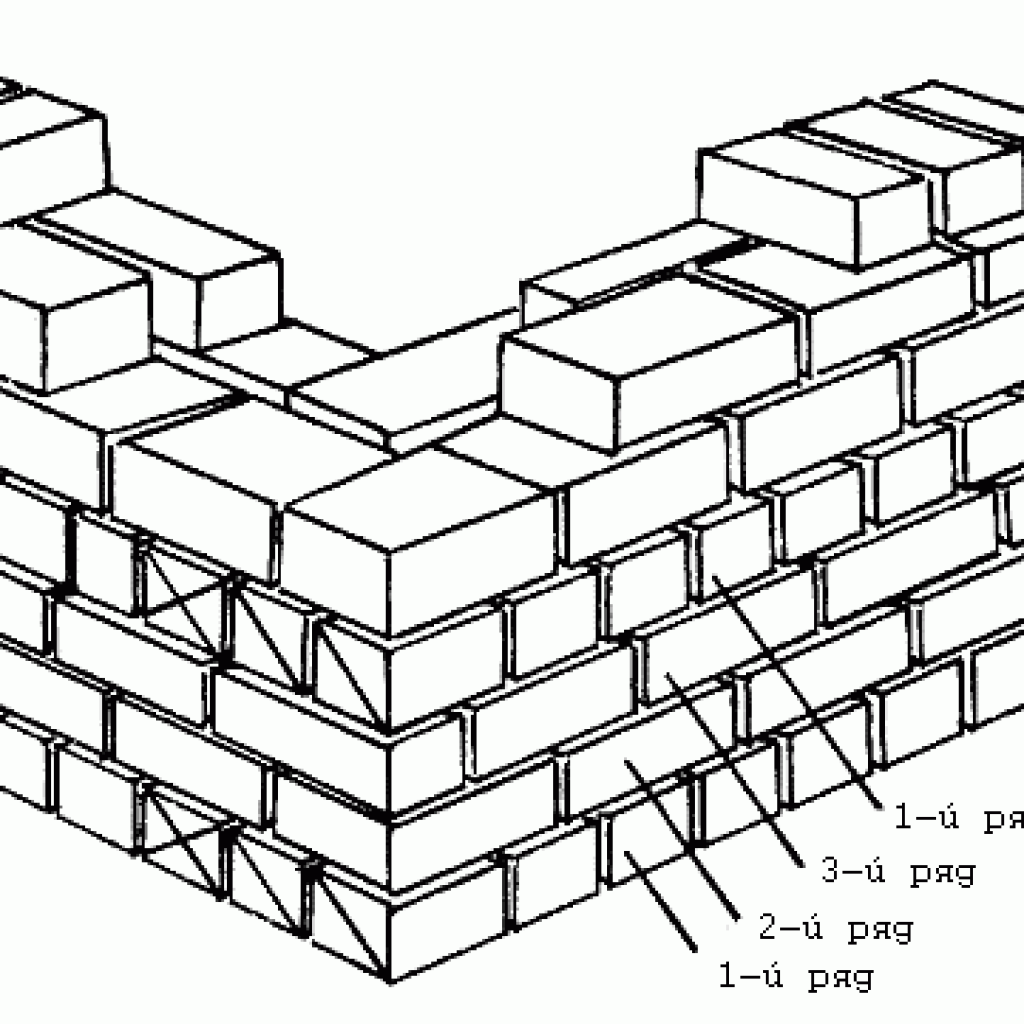
The thickness of an ordinary wall made from a single wall element will be 25 cm. The construction itself must be carried out according to a special algorithm. It is important to perform the initial dressing specifically for vertical moments. A brick located in a vertical row must overlap the vertical seam (it will be formed from its “brothers” from the bottom row).
The most popular types of installation systems are::
- in one row;
- in several.
In the first case, the lowest row will be laid with the spoon side out. But the row after it will also show the bonding surface. The transverse seam in this place seems to be shifted by a quarter of the brick, and the longitudinal seam by a whole half of it.
With multi-row, not every available row is alternated, but done after several. Typically, for single ones, this method will involve tying off those that are nearby (this happens every six). When practicing using a thicker analogue of spoon rows, there can be only five.
One and a half size
One-and-a-half masonry is the most common in construction. In this option, the brick will be placed at the corners. Moreover, in the first row the material is placed at a right angle. There is even a special scheme for this:
- The first row is laid out with a cord - it needs to be pulled between two bricks, the first and second bricks in height. In the first row, all elements should be directed with the spoon side inward.
- The next row is laid opposite to the previous one. The result should be a mirror image of what has already been laid down.
- The inner side will be made up of brick, and the outside will only have half of it. This will ensure sufficient structural strength.
Paved options
Brick walls have a number of advantages over other building materials. These are advantages such as, for example, low thermal conductivity and high strength. However, all these qualities can be lost if the wall has a thickness that is not optimal for the given conditions.
The thickness of a brick wall is a very important indicator, affecting not only the quality factor of the building structure and its load-bearing capacity, but also the consumer characteristics of the object (functionality, degree of heat, noise, vibration insulation, etc.).
Laying brick walls
Determining how thick brick walls should be is quite simple. According to standards, all red brick walls have a thickness that is a multiple of half its length, that is, 12 centimeters. The name of the wall is based on the same parameter:
- Half a brick;
- In one brick;
- One and a half bricks and so on.
A wall of half a brick is 12 centimeters thick, a wall of one brick is 25 centimeters, a wall of one and a half bricks is 38 centimeters, a wall of 2 bricks is 51 centimeters thick. The slight discrepancy between these figures and those that are multiples of 12, that is, 24,36 and 48, is due to the fact that concrete can be located between two layers of brick. Load-bearing walls and all external walls of the building, as a rule, are made of one and a half bricks or more. All partitions are made of half or a quarter brick.
The construction of brick walls in one brick is beneficial from the economic side. However, such walls cannot be built in all places, since there are sharp seasonal temperature changes. In this case, additional façade masonry with the device of a thermal insulation layer and an air cushion.
When constructing brick walls, as already mentioned, they try to make the load-bearing walls thicker; in addition, they are often strengthened by reinforcement.
Walls with variable thickness are allowed. For example, when constructing multi-story buildings, the width of the walls is often cut to half a brick after the fifth or sixth floor. This is done in order to reduce the overall load on the walls themselves.
Calculation of the thickness of a brick wall
All calculations of the thickness of a brick wall are made based on the size of an ordinary red brick:
- Length 250 millimeters;
- Width 120 millimeters;
- Thickness 65 millimeters.
The brick weighs 3.2 kilograms. 1 cubic meter of brick weighs approximately 1800 kilograms. The calculations also take into account the climatic features of the area. If in winter the temperature reaches -25 degrees, then the width outer wall should be 51 or 64 centimeters. If external insulation material is used, then it is allowed to make a wall 25 centimeters thick.
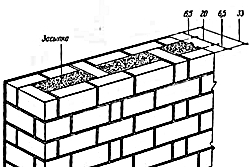
Construction of a wall with backfill
Knowing this feature of this building material, you can easily calculate the consumption of bricks for the construction of a particular house. Let us build a house in an area where there is severe frost. In this case, the walls will be erected without an insulating layer. Then the thickness of the walls should be 51 centimeters. This means that the laying will be carried out in two bricks.
Then knowing the parameters of the walls, that is, the length and height of all the walls, you can find out their area. For example, two walls will be 5 meters long and two walls will be 3 meters long. The total height is 3 meters, then:
5*3+5*3+3*3+3*3=48 square meters.
Now let's find the area of one brick. Since it is said that the masonry is carried out in two bricks (51 centimeters), then the area of one brick is found as its width multiplied by its height, that is, we have:
0.12*0.065 = 0.0078 square meters.
Now you can find the number of bricks to build a wall as the total area divided by the area of one brick and multiplied by two, since the masonry is made of two bricks, we get:
48/0.0078*2=12307 bricks.
Let's multiply this amount by the weight of one brick and get the total weight of all walls:
12307*302=39390 kilograms.
Now, knowing that one cubic meter of brick weighs approximately 1800 kilograms, you can easily find the required amount of red brick:
39390/1800=22 cubic meters.
If you find out the price of one cubic meter of brick, you can easily find out the total cost of constructing such a wall.
Brick walls and their use
Let's consider wall options.
External load-bearing walls
Smooth, neat wall laying
A brick wall that is folded into one brick can carry almost any load that is evenly distributed over its surface.
Despite all the advantages, there are also disadvantages. For example, the main thing is low heat-protective qualities. Wooden wall to maintain a temperature of, say, 30 degrees, a thickness of only 16-20 centimeters is needed. In this case, the thickness of the brick wall should be 64 centimeters.
In order to ensure normal temperature conditions, very thick walls must be laid. From the calculations it is clear that even for a wall of 2 bricks the consumption is simply huge. In order to reduce the cost of constructing warm walls, I use hollow bricks, or the same solid ones, but an air cushion is arranged between the masonry.
Various insulating materials are placed in this air cushion. The walls themselves are plastered inside with so-called warm plaster, that is, a special concrete composition. From this we can conclude that a solid wall made of 1.5 bricks, not to mention thicker walls, will not be profitable from an economic point of view.
Thickening the walls also leads to the need to make a stronger foundation, which will also affect overall costs. It is for this reason, as previously noted, that air cushions are made between the walls. The width of such an air space should be at least five centimeters; as a rule, it is made on the edge of a brick, that is, approximately 6.5-7 centimeters. With such a wall arrangement, even with a fairly small width, the house retains heat, and the brick consumption is reduced by 15-25 percent.
The second way to reduce the width of brickwork is to insulate the walls using felt. When using it, the efficiency of walls in terms of heat conservation increases by 20-30 percent. If you use a layer of foam plastic instead of felt, you can achieve a twofold or more increase in efficiency. The following materials are also used to preserve heat:

Unfortunately, improperly laid brick walls are prone to cracks.
- Mortar based on fine aggregate or slag;
- Perplite;
- Sawdust and so on.
All these materials increase the heat-insulating properties of a brick wall by 10-15 percent.
The most economical wall construction is considered to be well masonry. It consists of two separate half-brick walls, which are located at a short distance from each other. The walls have connections with each other, which are made in the form of horizontal and vertical brick bridges. These bridges form closed wells, hence the name of the masonry technology.
During laying, the resulting wells are filled with expanded clay, lightweight concrete or slag.
With continuous masonry, it will be more economical to install a layer of insulation on the outside or inside of the wall. In this case, a brick wall can have almost minimum thickness, which is determined only by a given strength coefficient, as a rule, a wall of 25 centimeters is quite sufficient for almost any load.
In turn, the issue of thermal savings falls entirely on the insulation, or rather on its parameters such as thickness and quality. It is only worth noting that if the insulation is located outside, then it is worth protecting it from precipitation and mechanical influences, which can be done by plastering the insulating layer. If the insulation is located on the inside of the wall, then care should be taken to ensure that it does not get wet, that is, a vapor barrier needs to be installed.
As for the thickness of the wall, which will be made of effective brick, it can be anything, and in this case it does not depend on whether there is an insulating layer or not.

Walls by sculptor
When constructing brick walls and choosing their thickness, you should pay attention to the fact that brick has a high degree of thermal inertia. This means that a wall made of red brick cools down very slowly and also heats up slowly.
Therefore, in houses made of brick, temperature changes during the day are very insignificant. However, if the wall is made thick enough, it will take too much fuel to warm it up, especially if it has been standing in the cold for a long time. Such cases are possible when constructing red brick houses that are used as summer cottages.
Internal external walls
Internal walls are usually made of solid brick. The width of such walls is usually 25 centimeters. In this case, pillars with a side length of 38 centimeters are used as support. If we are talking about piers, then the thickness of such walls should be the same, but the pillars should have a side with a length of 51 centimeters. In cases where there is a large load on the piers and the pillars themselves, they can be reinforced. In this case, steel reinforcement with a diametrical cross-section of 3-6 millimeters is used.
The partitions themselves, if they are short enough, up to 1.5 meters, can be laid out in half a brick, that is, the thickness will be 12 centimeters, or a quarter of a brick, that is, the thickness is 6.5 centimeters. If the wall is more than 1.5 meters in length, and it is lined with bricks on edge, then reinforcement is used to increase its load-bearing capacity.
Reinforcement is carried out with steel reinforcement 2-5 millimeters thick. In this case, the wire is laid every 2-3 rows of bricks.
The walls themselves are often laid out on cement-sand or cement-lime mortars, less often on cement-clay mortar. Cement-sand mortar For interior walls is not optimal, since when hardened it has excessive strength, which does not depend on the brand of cement used. Therefore, it is better to add lime or clay to it. Such a solution becomes more flexible and economical, since its consumption is reduced by 1.5-2 times.
Industrially produced cement, as a rule, belongs to the M300-M500 grade. This very lime dough, which is prepared from slurry lime, is poured into it.
Walls made of foam blocks

Wall masonry
As already noted, the biggest disadvantage of red brick is its poor thermal insulation quality. On modern stage construction, on the market building materials A relatively new material has appeared that completely eliminates the problem of thermal insulation - this is a foam block.
The foam block is produced using sand, cement, foam, that is, it is an environmentally friendly material. The shape of the foam block resembles an ordinary cinder block, only the former is much lighter.
The foam block has excellent thermal insulation due to the fact that it itself consists of pores in which there is air, that is, it contains both building material and an air cushion in advance. There are several foam blocks different types, however, they all have the same name - cellular concrete.
When building the walls of a house, ordinary standard foam blocks are used, which have the following dimensions:
- Length 600 millimeters;
- Width 300 millimeters;
- Height 200 millimeters.
Based on this, we can judge what thickness of the wall should be obtained from foam blocks and bricks when in different ways their installation. If the thickness of the wall is measured by half a brick, then with blocks the situation is different. For example, there is no such type of masonry as in the floor of a block.
If the block is laid on edge, then the thickness of the block wall will be 200 millimeters. If the block is laid in the usual way, then the width of such a wall will be equal to 300 millimeters. The block is not laid across the foundation - this is a waste of material and money. A block wall thickness of 600 millimeters has excessive thermal insulation properties, which are not required to such an extent, even in severe frosts.
As a rule, the block is laid on edge, resulting in a wall thickness of 200 millimeters. After this, interior finishing is carried out. Which can be produced by plasterboard. Guides are nailed to the blocks indoors and sheets of drywall are attached. Such a wall will perfectly retain heat inside the house and keep out the cold from the street.
As for the production technology of masonry, it is similar to brick. In essence, a foam block is a brick, only in larger sizes. The foam blocks are fastened together using cement mortar.
Walls are not laid in two rows of foam blocks, for the same reason that we discussed above.
Another advantage of foam blocks is their lightness, despite large sizes. The weight of one foam block with the dimensions indicated above is approximately 25-30 kilograms. This makes it possible to save money when building a foundation, which can be chosen to be of a simpler type and structure, which in turn will require lower costs.

Brick wall
The last advantage is ease of use. The foam block has a fairly large margin of safety, but at the same time it is very easy to deform and give it almost any shape, which allows you to easily lay walls.
Load-bearing walls are laid as a whole block. When laying partitions, it is allowed to saw the block in half. A wall lined with such blocks will have a width of 10 centimeters. However, this is not always possible. If the wall has relatively small dimensions, that is, no more than 2 meters in length and no more than 3 meters in height, then this method is allowed; if the dimensions exceed those indicated, then no. This is explained by the fact that it is almost impossible to cut a foam block perfectly evenly, especially at home without special equipment. Therefore, the walls will not be perfectly smooth, which can lead to collapse if they are large.
It is also worth noting the fact that walls made of foam blocks are never subject to fungal growth.
10*5=50 square meters – 50/0.0078=6410 – 6410/563=12 cubic meters of brick, then for a wall with the same parameters made of blocks you will need 278 blocks, which is equal to approximately 10 cubic meters. In this case, the wall will have the best thermal insulation properties than from brick. It should also be noted that the cost of one cubic meter of foam blocks is less than the cost of a cubic meter of red brick. The benefits will also be noticeable during laying. This refers to saving the binder, which is usually a sand-cement mortar.
- What wall thickness can be
- Thickness load-bearing wall and partitions
- Methods for reducing the thickness and improving the insulation of brick buildings
The thickness of a brick wall is calculated taking into account climatic conditions. The more severe the weather conditions in the construction area, the thicker it should be brickwork, which is designed to effectively retain heat in the house. The thickness of the external walls depends not only on what kind of brick will be used in construction, but also on whether it is planned to use modern insulation in the finishing of the building. Ceramic and silicate products used for construction are solid and hollow, and this division affects the thickness of the walls being built.
When using a full-bodied product, they are made thicker. If hollow ones are used, then the thermal conductivity of the building being constructed is reduced due to air chambers, and the thickness of the walls may also decrease.
When making a building from sand-lime brick, thinner outer walls are erected, because this type of building material has lower thermal conductivity compared to a ceramic product.
Recently, developers have begun to abandon the construction of thick walls. To reduce thermal conductivity, various insulation materials are used, which reduce the cost of the structure and increase its soundproofing characteristics. When using insulation, the optimal wall thickness is such that it can withstand all the loads, and the constructed structure will be durable.
What wall thickness can be
To determine the required value for the walls of the house, you need to refer to SNiP II-22-81. It establishes the thickness of brick walls, external and internal load-bearing walls and partitions. The thickness must be a multiple of 12 cm.
This is the width of a standard brick, and this number is approximately ½ part of its length, which is 25 cm.
Therefore, the construction of a structure with a 12-centimeter thickness is called half-brick masonry, and one-brick masonry, accordingly, will be equal to 25 cm. The thickness of walls laid with one and a half bricks will be equal to 38 cm, two - 51 cm, and two and a half - 64 cm.
The choice of masonry depends on how much the thermometer drops in winter. If the air temperature drops to -30°C, then you need to lay a thickness of 2.5 bricks, or 64 cm. The weight of such masonry will be very large, and the cost of creating a foundation will be enormous.
Therefore, in areas where there are severe winters, the construction of external walls of two and a half bricks is not used. Such construction requires a large consumption of materials and significant financial investments. Buildings in such areas are built with one and a half or two bricks. They are strong enough to withstand floors during the construction of a building of several floors. To increase strength, masonry reinforcement is used every few rows. The use of iron wire ensures the solidity of the structure and prevents cracking of surfaces.
Load-bearing external walls have an average masonry thickness of 38 cm. Their construction from brick allows the masonry to fulfill its purpose in full. They take on the load of the roof, upper floors, partitions, and also protect the building from the influence of the external environment.
The use of hollow ceramic stones, the size of double bricks, for the construction of external walls is becoming increasingly widespread. If they are used for masonry in one block, then the strength and thermal conductivity will correspond to 51 cm. Using lightweight products, the pace of construction is significantly increased and the consumption of mortar is reduced. Lightweight blocks of large sizes have less weight, and a lighter foundation is required for such masonry.
A brick wall thickness of 25 cm will be sufficient in the middle zone if you use insulation. Ceramics and silicate are durable, reliable building materials with excellent load-bearing capacity. The masonry, folded into one brick, is capable of impeccably holding any load.
Reinforced concrete, wood and concrete floors can be supported on a supporting structure, the thickness of which is 25 cm, and several floors can be built on top. Cold walls can be insulated with polystyrene foam or high-quality mineral wool, obtaining the “thermos” effect. With this covering it will be warm in winter and cool in summer. In this case, the brick serves to create a strong and durable frame.
Return to contents
Thickness of load-bearing walls and partitions
When laying load-bearing interior walls and partitions, silicate is often used because it is much better than red ceramic in terms of soundproofing characteristics.
Its masonry is done in the same way as ordinary clay bricks. The internal partition, which carries an additional load, must be 25 cm thick, otherwise it will not withstand the load. Interior partitions, the purpose of which is only to divide the inter-apartment space, are made in half a brick, and this is often enough. The thinnest partitions have a thickness of 6.5 cm. To achieve this thickness, it is enough to lay the brick on its edge. Thin partitions with a length of more than 1.5 m are equipped with reinforced wire.
If such thin internal walls require increased sound insulation, they are finished with special sound-absorbing materials. Cork and foam sheets are suitable for this.
To reduce the load on the base and reduce the overall weight of the entire house, hollow bricks are used for partitions.
Brick is a popular and in demand material in construction. It has excellent performance characteristics. Reliable material can withstand significant loads from floors, ceilings and roofs. Its advantages include low thermal conductivity, high strength to deformation and bending, long service life, and sound insulation. Brick building no massive foundation required. The thickness of the external brick walls affects the load-bearing capacity of the building. Next, we will consider the established standards that are relevant today.
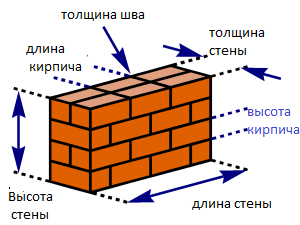
Brick wall parameters
The thickness of the walls of a house can vary over a wide range - 12 - 64 cm. The most common thickness is 2 bricks. This masonry is highly stable and reliable. The thickness of the brick wall according to GOST should provide the building with maximum strength.
The state standard regulates that when constructing residential buildings with up to 5 floors in a temperate climate zone, the minimum thickness of the supporting structure should not be less than 51 cm.
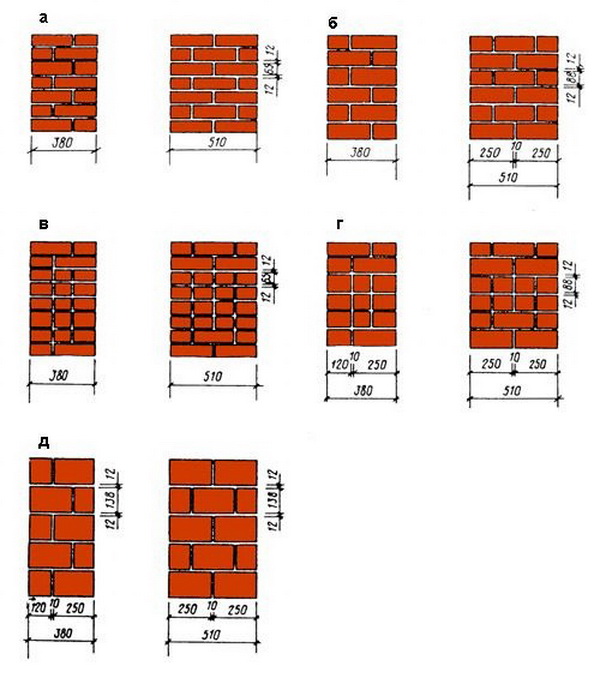
Nuances of choosing the type of masonry
When choosing the type of masonry, builders take into account the following factors:
- Load. First of all, it is necessary to take into account the number of floors of the building.
- Climate zone. It is important that the building is warm in winter.
- Aesthetic component. Thin masonry looks more elegant compared to thick masonry.
- Compliance with standards. The structure must be safe to use.
For internal load-bearing walls, masonry with a thickness of 25 cm is used, which corresponds to one brick. For partitions that serve to divide rooms into zones, 12 cm is sufficient. The rigidity of such a structure is imparted by reinforcement with ordinary wire, which is placed in the seams.
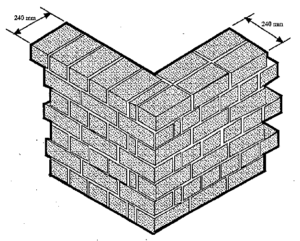
Single brick masonry
When the temperature drops to -30 degrees in winter, keeping the house warm is a task that 64 cm masonry successfully copes with. However, it should be taken into account that the weight of the structure increases and a more massive foundation is needed.
When building a residential building in the southern region, a masonry scheme of 1.5 bricks can be used. If you need to build a barn or other utility room, then laying one brick is enough.
Which material is best for construction?
The modern construction market offers bricks: double, single and one-and-a-half. The dimensions of a single brick are 250 x 12 x 65 mm. The one-and-a-half standard size is 250 x 120 x 88, and the double size is 250 x 120 x 138. If you choose the most effective material from an economic point of view, then it is more profitable to take the last two standard sizes. High-quality materials are used to construct the base.
Having calculated what the thickness of the brick wall should be, all that remains is to select the right material:
- Unlike ceramic solid bricks, hollow bricks are specially left with voids inside. These products are produced by ordinary workers and cladding.
- Porous ceramic blocks can provide excellent thermal insulation properties. This is an ideal option to save on the use of insulation.
- Refractory fireclay bricks perfectly withstand high temperatures. It is used to lay out fireplaces and stoves.
- White sand-lime brick afraid of exposure to moisture and temperature fluctuations.
- Hyperpressed brick is highly durable. It does not absorb steam and does not allow moisture to pass through.

Improving thermal insulation properties
The thickness of a load-bearing brick wall is often increased through the use of insulation. Its use in internal construction is in demand, as it has many advantages. The thickness of the load-bearing wall can be increased slightly depending on the choice of thermal insulation materials. Insulation also needs to be carried out outside the structure. Consider the construction pie:
- The thickness of the outer part of the structure with masonry of 0.5 bricks is 12 cm.
- The insulation is selected taking into account the climatic region.
- The thickness of the internal part of the structure must be at least 25 cm. The building materials are blocks or bricks.
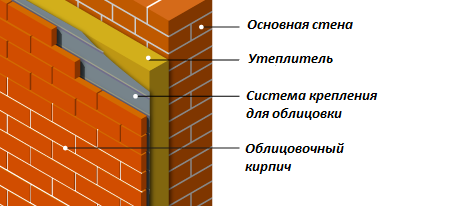
The thickness of the supporting structures, regardless of the choice of material, must be no less than that specified in GOST.
Calculation of material consumption
After completing the construction plan, the surface area is calculated based on the dimensions of the walls:
4*3+3*3+4*3+3*3=42 m2
You need to calculate the area of one block. Based on the calculation that the masonry will be built in one brick, the parameter can be easily found by multiplying the width by the height:
0.12*0.065 = 0.0078 m2.
1 m3 of brick weighs approximately 1800 kg. Based on this, you can make a calculation of what the number of bricks should be for the construction of a particular object.
5385/1800≈3 m3
Let's summarize. According to GOST, the wall thickness must be no less than the specified standards. The indicator varies: it is influenced by the climate zone, as well as the type of building. If the construction project was developed by professional specialists, then you can calculate the consumption of the main building materials yourself using the numbers from the diagram. Correctly performed calculation allows you to reduce costs during the work process. You can buy the required number of blocks at once to avoid unnecessary material waste. On the other hand, the exact number of bricks will allow you not to purchase additional building materials after the start of construction work.
How to reduce the thickness of buildings and improve thermal insulation
People planning to build their own housing with their own hands may be interested in the answer to the question: “What thickness should the structures have in order to maximize the thermal performance of the building and its insulating properties?” As you know, constant noise has a bad effect on a person’s overall well-being. The problem of good sound insulation is most pressing for those who live near a train station, airport or factory.
Brick walls with an air cushion provide effective protection against noise. The technology is called well masonry. Between the walls of the house, 25 cm each, an empty space is left, which is filled with porous material:
- light concrete mixture;
- slag;
- organic insulation;
- expanded polystyrene;
- expanded clay.

A cavity filled in this way makes it possible to reduce the overall weight of the structure and increase the level of thermal insulation.
To create an insurmountable barrier to cold from the street, you will need to make a ventilated façade. For this purpose, special heat-insulating panels, plasters and various facing materials are used.
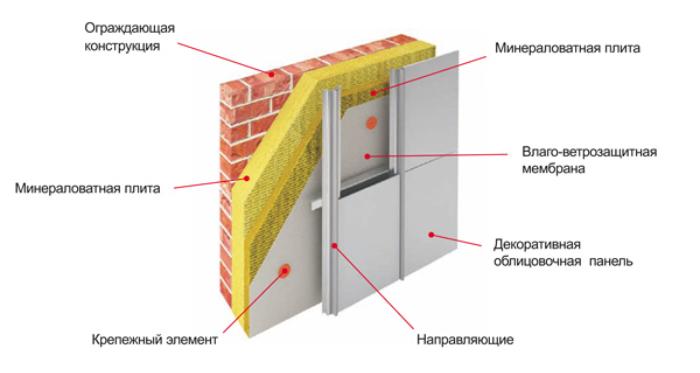
Installation of a ventilated facade
The masonry of the outer wall 25 cm from the outside is finished using facing bricks, and from the inside the structure must be insulated.
The following scheme is proposed:
- On the inside, the brick walls of the house are sheathed with insulation.
- The insulation layer is covered with a vapor barrier film.
- A metal mesh is laid on top and plastered. Alternatively, you can use drywall.
- Perform interior decorative finishing. Its task is to close all previous layers of the “pie”.
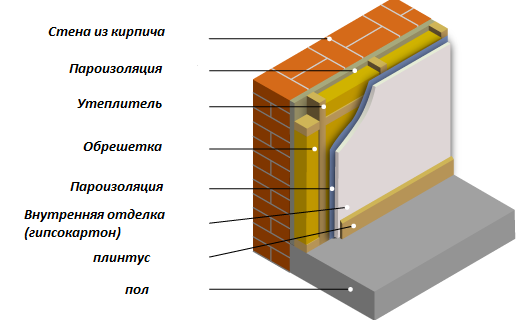
The result is cheap and cheerful. With the right approach, a practical owner will be able to reduce the initial cost of the property by 20%.
Building materials should not be used in areas of high seismic hazard. During a strong earthquake, the masonry is destroyed to the foundation.
What owners of suburban brick residential buildings need to know
Laying the walls of dacha buildings with two bricks is an excellent design solution for the Siberian winter, if combined with insulation of structures outside and inside. It is profitable to build such a construction project from an economic point of view.
When choosing which wall thickness is most suitable, we must not forget that a building material that has high strength also has great inertia. This means that it is best to build buildings from bricks for permanent residence, where temperature changes during the day are insignificant. Owners country houses made of brick, they should know that it will warm up slowly if in winter the owners do not live in it permanently, but only come from time to time.
Residential buildings made of brick will serve their owners for a long time. They are warm in the cold season and cool in the summer.
Our article would not be complete without a video. Watch a video about brick walls:
It is important for builders to know what thickness of a brick wall according to GOST should be in a given case. Brick is one of the most common and familiar materials. Currently, houses and other permanent structures are being built quite often. The thickness of the brick wall itself can vary significantly depending on its purpose (fence, load-bearing wall, etc.). The most common thickness is 2 bricks, as it is highly reliable and stable. In addition, the construction of brick walls does not require a powerful and massive foundation.
In addition to these advantages, the material also has good thermal insulation properties. All these factors allow the material to maintain its leadership and remain popular in the construction of houses and outbuildings. There are various types of this material, which differ in properties and price. However, the quality of even the cheapest brick remains quite high, as do its strength characteristics. Next, we will consider what the thickness of a brick wall should be when constructing certain objects, as well as some technologies for constructing brick walls.
Selection of masonry type
In order for buildings to be strong and reliable, before starting construction it is important to take into account a number of factors in the project:
- First, the loads that will affect the masonry (wall) are calculated. Usually the calculation is carried out for a specific building.
- Climatic conditions also affect the strength and reliability of the structure. At the same time, the masonry of the load-bearing wall of the house must not only be strong, but also have thermal insulation characteristics.
- Appearance. Artificial stone materials usually look very attractive, so landscape designers often use them when designing objects.
The thickness is usually regulated state standard. During construction, it is very important that the walls comply with GOST. On at the moment the construction of facilities is regulated by the following standards: GOST R 55338-2012 (Masonry and products for it) and GOST 2 4992-81 (Method for determining the adhesion strength in masonry). At the moment, the thickness can be in the range of 0.12-0.64 m.
The thinnest masonry is ½ brick, it is 0.12 m. This type of masonry is used for the construction of small fences (when delimiting an area) and interior partitions. The masonry of 1 brick has a thickness of 0.25 m. It is often used in the construction of fences, fences, sheds and other auxiliary buildings. The construction of 1.5-layer brick walls is quite common in the southern regions of the country. Their thickness is 0.38 m. More durable masonry - 2 ½ (0.51 m) and 2 bricks (0.64 m) - are designed for harsh climatic conditions.
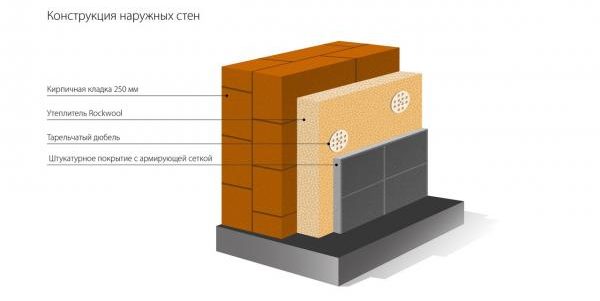
At the same time, load-bearing walls for objects built in a temperate climate should have a thickness of 0.51-0.64 m. Often during construction they are additionally insulated using various natural and synthetic insulation materials.
For outbuildings and other auxiliary buildings, 0.38 m of masonry is usually sufficient. However, for the load-bearing wall of a residential building, a thickness of 0.51 m should be provided. In this case, it is allowed to reduce the thickness of each subsequent floor in a multi-story building. For example, for the first floor the wall should be 0.64 m, and for the 5th-6th floor the supporting structure can be made 0.51 m. In this case, the difference in thickness is hidden by thermal insulation.
For buildings up to 5 floors high, GOST recommends a minimum thickness of load-bearing structures of 2 bricks, and for commercial non-residential buildings (one-story) the recommended thickness of the structure is 1.5.
For walls located inside the building, the standard defines the following:
- load-bearing internal structures must have a minimum thickness of 0.25 m (1 brick);
- for dividing partitions (which are not subject to loads and serve as dividers), half-brick masonry is acceptable.
However, in order for a half-brick wall to be rigid, it must be reinforced with metal wire. This is a must.
Material selection
At the moment, the industry produces single, one-and-a-half and double bricks. The dimensions of the standard (single) are 0.25 x 0.12 x 0.65 m. This standard was adopted in 1925 by the domestic standardization system. A little later, one-and-a-half and double standard sizes appeared - 0.25 x 0.12 x 0.88 m and 0.25 x 0.12 x 0.138 m, respectively. At the same time, one-and-a-half and double ones are more economical.
Thus, for a load-bearing structure of 2.5 bricks, it is economically beneficial to use double and single facing bricks. At the same time, they always try to make the cladding single: such masonry has a more aesthetic appearance. If only a single product is used for such masonry, you will have to pay about 30% more for the material.

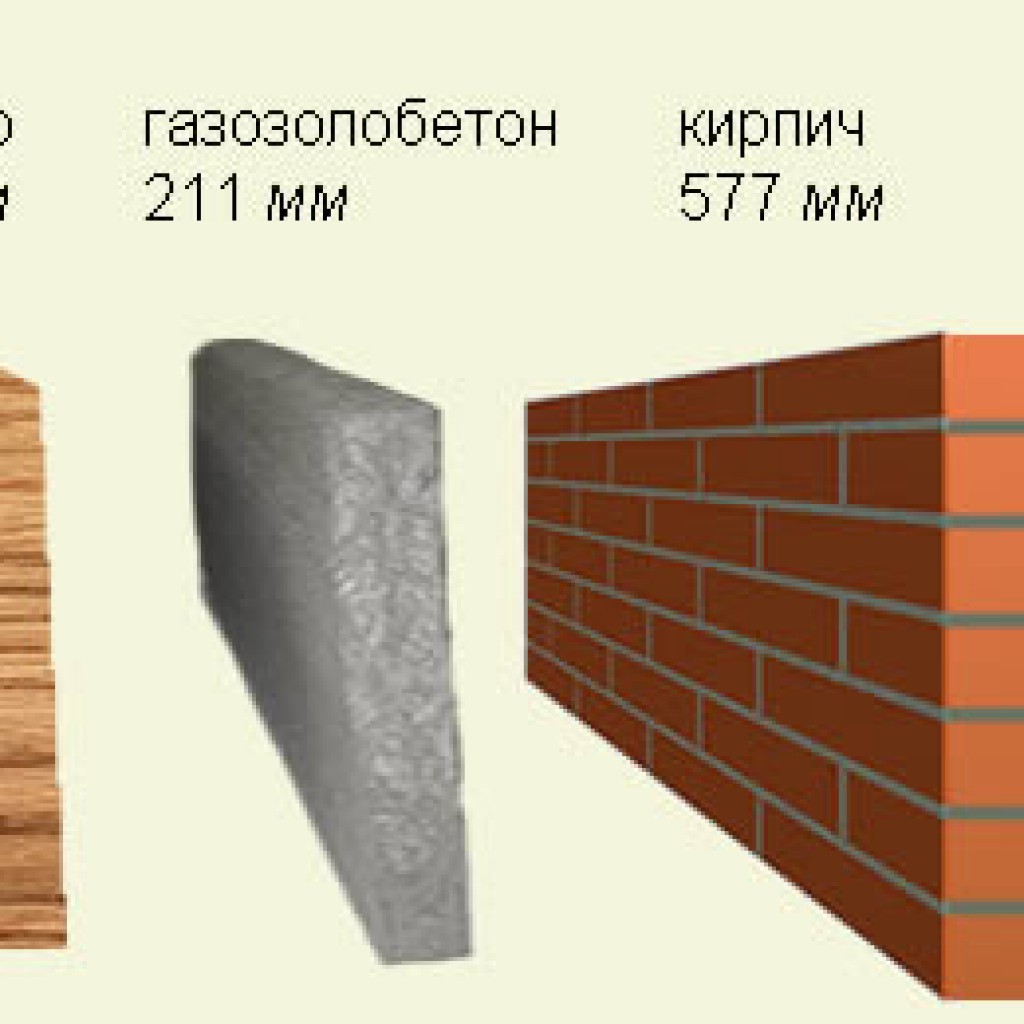
One of important functions brick walls is thermal conductivity. Although this building material has a relatively high value, it is significantly lower than that of a number of other building materials. In this indicator, brick is significantly inferior to wood or foam concrete.
However, the thermal insulation properties can be significantly improved by using hollow versions of the cladding material. It is completely impossible to use hollow material for the construction of load-bearing structures; it is significantly inferior in strength to solid material.
Also, hollow materials cannot be used in the construction of foundations, bases, plinths, etc.
In conclusion: about the benefits and increased thermal insulation properties
Due to the low cost of materials such as brick, it is economically feasible to construct walls with a thickness of more than 0.38 m. In this case, the costs of materials and work can be reduced by at least 20%. However, the question often arises about insulating the room.

One of the insulation options is the use of masonry in the form of wells. To do this, a gap of about ½ brick is left between the rows of masonry, which can be filled with various insulation materials. It doesn’t have to be filled, then the air gap will act as insulation. However, filling this gap with foam concrete will significantly increase not only the insulating characteristics of the structure, but also its strength. This gap is often filled with expanded clay mixed with cement mortar.
When building houses, it should be remembered that brick is not recommended for use in seismic zones; during an earthquake, the masonry very quickly collapses to the ground.
 Civil service in the navy
Civil service in the navy Why does an ex-boyfriend dream: the meaning of sleep in dream books
Why does an ex-boyfriend dream: the meaning of sleep in dream books Dream Interpretation: Why do you dream of a garden? I dreamed of a green garden
Dream Interpretation: Why do you dream of a garden? I dreamed of a green garden