How are load-bearing walls located in houses? What determines the minimum thickness of a brick wall? Ways to improve heating technology and insulation of brick buildings
Brick is one of the most ancient inventions of mankind. Water, sun and clay combined with the enthusiasm of the first craftsmen created artificial stone amazing strength, reliability and durability.
Such brick structures as the Moscow Kremlin, the Winter and Smolny palaces, and the Peter and Paul Fortress have survived more than one century. But their share included hard times of war, frosts, floods and fires. But to this day there is no need to restore them brickwork.
Distribution of loads on the ground
Running shoes can be made on fairly stable and homogeneous soils. Drills can be used on fragile soils, but without water. Make ditches for crosses. Then drop in a 10mm layer of crushed No. 2 stone and mix well with the pestle. Then scrape the bottom with cement and sand to keep it clean and level.
Freemasonry system of fencing
Against this background, place three 10mm thick steel rods, tied every 20cm with 5mm rods. The weight of the house is carried by the walls to the foundation and then distributed over the ground. Posts are small posts built into walls. The blanks collect the weight of the tiles, walls and roof and transfer them to bales, which receive these concentrated loads from the pedestals and distribute them evenly across the base.
Today, when the market is overflowing with construction miracles, brick is still in fashion, it is still the number one building material. Its excellent load-bearing capacity allows the walls to withstand heavy loads created by concrete, reinforced concrete, and wooden floors of multi-story structures.
At the same time, brick is inferior to many wall materials in terms of heat and sound insulation qualities. For example, when it is -30 ° outside the window (and in Russia this happens quite often), the thickness of the external walls made of solid brick should be 64 cm. Whereas under the same climatic conditions, the sufficient thickness of the cobblestone walls is 18 cm.
The next episode of the series here provides specific preparation information. This is an informative article, if you have any questions, ask a professional. Process used: wall mantle in facing bricks, laid joints.
Double insulated brick wall: thermal, aesthetic and durable choice. 
Now he controls all the edges and, of course, is very interested in insulating the outside. This double wall technique combines an exposed brick wall with a masonry or concrete wall. The space between these two walls is occupied by a layer of thermal insulation - here it is semi-rigid mineral wool- and an air knife. The outer brick wall is attached to the inner wall of the structure with metal fasteners distributed over the surface.
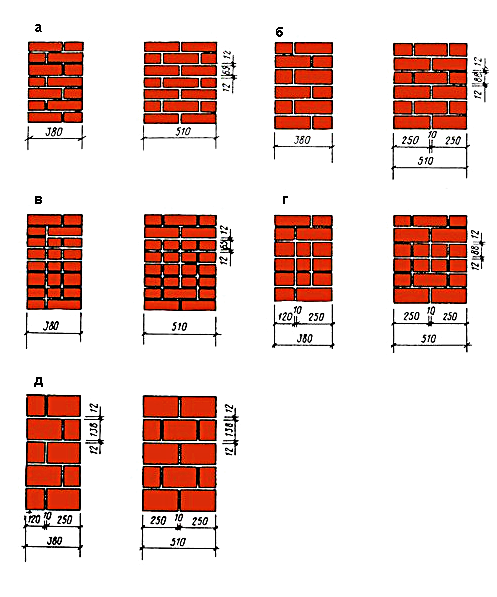
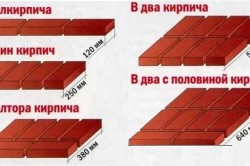
As you know, the thickness of brickwork is measured by the number of bricks laid along the thickness of the wall, and is a multiple of the standard brick parameters (6.5 x 12 x 25). Masonry of 12 cm is usually called masonry of half a brick, 25 cm - one brick, 38 cm - one and a half bricks, 51 cm - two bricks, 64 cm - two and a half.
These walls are more expensive, but have many advantages: perfect waterproofing, high sound insulation, high thermal insulation, good thermal inertia and intervention from the outside during renovations. The only problem, according to Philippe Hosse: “Thermists don’t know enough about these methods.” Result: Depending on the location, the insulation thickness recommended by the thermal study differs from the equivalent thermal performance. Likewise, thermal engineers would not yet have sufficiently taken into account the thermal inertia of the wall, the air gap and the surface attenuation coefficient associated with the color of the brick.
However, thickening brick walls significantly increases the load on the base of the building, which inevitably affects the construction budget. How to increase the thermal conductivity and insulating qualities of brickwork without resorting to excessive weighting? What should the thickness be? brick wall? Experts say that its choice depends on the purpose and location of the wall.
For Philippe Josse: “This situation will improve over time as these products become more widely distributed.” An option that allows him to solve three problems: thermal, of course, but also aesthetic and relatively sustainable. “Brick veneer offers greater durability, weathering and does not require repainting.” To improve the aesthetic appearance, the architect also wanted to create a joint installation. With the help of these bricks, the installation is carried out with a special adhesive mortar, which allows thin horizontal joints to be made into a recess of the outer bare one, the vertical joints remain open.
Internal partition of the building
However, this is not enough for good sound insulation. To prevent extraneous sounds from entering the house, you should resort to one of three methods:
- increase the thickness of the masonry;
- apply additional material with sound-absorbing properties;
- use “on edge” masonry, when the brick is laid on its edge, which achieves a wall thickness of approximately 7 cm. If the length of a thin partition exceeds one and a half meters, it should be reinforced with reinforced wire.
Internal load-bearing wall
Soaking is easier, removing cement and reducing cleaning operations. In this project, the company and the architect worked together to solve technical problems: At the request of the architect, we had two real-size prototypes with two types of frames developed for the window frames.
This helped us evaluate installation methods and decide possible problems. Fuel blocks with smooth wall. Good tools are needed to achieve good result. The main dimensions of the blocks are 60 cm in length and 25 cm in height. These dimensions are the same for all manufactured blocks. To build 1 m² of masonry, 6.67 blocks are required, regardless of their thickness. This is a very functional and economical solution for partitions. They have many advantages over classical barrier methods.
The thickness of the internal load-bearing wall of the house is 25 cm, or one solid brick, and can withstand any load from the roof, ceilings and other structures. An exception to this rule is a brick wall on which floor slabs are joined. In this case, single-brick masonry is unlikely to be sufficient.
External load-bearing wall
These two systems are the basis upon which many others are built depending on the types and layers of drywall and wool collected, the type of profiles and the like. elements. Depending on the requirements for humidity and fire resistance, sound insulation, thermal insulation, etc. the most suitable system is used. There are special systems such as an armored wall and much more.
In general, the rule of "more is more" applies to partition walls. Naturally, the wall is with 3-layer plasterboard on both sides of a double structure with 20 mm. insulating wool has much better performance than solid single coat plaster.
An external wall 25 cm thick will completely cope with its load-bearing mission. However, solid brick cannot cope with heat retention without additional insulation. Otherwise, in winter, at low subzero temperatures, the walls will begin to get wet.
Increasing the wall thickness to 64 cm, as already mentioned, is expensive in all respects.
The main goal is to visually divide the room. In this case, a one-sided wall of one structure is sufficient. Internal walls. Minimum, two layers of plasterboard, single structure, 6 mm mineral wool, total wall thickness 12.5 mm. External walls. Minimum, two layers, one structure, 10 mm mineral wool or 5 mm stone, total wall thickness 15 mm.
Seals forming bathtubs and other wet areas. Minimum, two layers of moisture-resistant plasterboard from the bathroom, single structure, 6 mm mineral wool, total thickness 12.5 mm. Walls through which plumbing fixtures or other large-diameter installations will pass. This most often occurs in bathrooms and various types of service areas. Then we use a double design.
 The situation can be optimized by using hollow bricks in the masonry. Masonry should be carried out with the formation of wells, voids and widened seams. In this case, the thickness of the brick wall will be reduced to 51 cm due to voids. With their help, its thermal conductivity properties will also decrease somewhat.
The situation can be optimized by using hollow bricks in the masonry. Masonry should be carried out with the formation of wells, voids and widened seams. In this case, the thickness of the brick wall will be reduced to 51 cm due to voids. With their help, its thermal conductivity properties will also decrease somewhat.
Walls with various openings, niches, shelves, etc. It is advisable to have two layers of drywall. In drywall systems, every element is necessary, and in partitions this is especially true. The precise execution of individual elements and the choice of materials are extremely important.
Frequent installation failures. There is no soundproofing tape on the edge profile. This strip is necessary for sound insulation, reduces vibration, etc. Mineral or stone wool is not reinforced enough, which causes it to slip. When we have two or more layers of drywall, each one will cover the joints even though they won't be visible.
To achieve 100% thermal insulation, you cannot do without in-wall insulation. It should be borne in mind that experts do not recommend insulating a brick wall from the inside of the room. This is done either outside or inside the wall.
The recommended brick wall thickness in this case and the type of insulation depend on the region of residence. Exterior wall can be insulated with light concrete mixture, expanded clay, expanded polystyrene, slag. In addition to effective insulation, warm solutions should be used - both masonry and plaster.
Distorted roughness of profiles. Each profile manufacturer left a factory hole with acceptable dimensions for switching electrical and other installations if installation is required larger size, double-skinned walls or additional elements in a single-structure design are made.
Advantages of plaster partitions
Extremely lightweight, allowing new buildings to be laid with little load-bearing structures, as well as breaking up rooms in old buildings with broken structures, etc. fast productivity without wet processes. Imagine having a living room that you already think is great, or having to bargain for other considerations. One week of masonry, painting, plastering, painting and another 2-3 days after cleaning. With partitions, all this can be done in 2 days. Extremely accurate size. You can make your own bathroom and then you won't even have to cut the tiles. Possibility for decorative elements. Oval openings, arches, niches, shelves and whatever you want. This makes the construction of electrical and plumbing installations much easier. Finished look. The partition, once installed, requires only an inexpensive coating and is ready for the final process. The classic method requires masonry, plaster and primer of at least 3 layers.
- One of the most important advantages.
- On the contrary, very little is “heard” if the correct system is properly implemented.
- Better thermal insulation.
The result is a dense “three-layer cake”, where:
- layer no. 1- the outer part of the wall is half a brick thick, that is, 12 cm;
- layer No. 2- insulation of the appropriate type and thickness;
- layer No. 3- the inner part of the wall is made of blocks or bricks 25 cm thick (to ensure load-bearing capacity).
This method of building a brick wall has three benefits:
They are used for the construction of load-bearing or non-load-bearing external and internal masonry in the construction of public and residential buildings, single or multi-apartment residential buildings, residential buildings, business centers, kindergartens, hospitals and other public buildings or commercial purposes.
This quality control guarantees the superior properties of the products when used correctly. Design standards for 40 dB noise protection for residential partitions. This does not interfere with the depth of the skull and does not reduce the strength of the bricks. Heavy suspensions can be made using suitable fasteners; The fastening of external thermal insulation is reliable and does not allow the thermal insulation boards to be disconnected during the operation of the buildings, which guarantees the integrity of the external plasters.
- reduction of material costs;
- reducing pressure on the foundation;
- expanding the living space by reducing the thickness of the walls.
Building facade
Insulating the façade will also help improve the insulation and thermal performance of a brick building. This can be achieved in the following ways:
- conventional insulation of the facade, followed by its cladding or plastering;
- arrangement of a ventilated facade using siding, lumber, thermal insulation panels, plaster, and facing bricks.
By listening to the advice of experts, you will build brick house for the neighbors to enjoy and for themselves. It won't resemble a massive pile of bricks. But at the same time it will become a reliable fortress for you - warm, quiet, cozy. It will be possible to live in this fortress house without bothering for several decades or even longer.
They are also indispensable for the renovation and renovation of existing facilities. For short time The company's economical and environmentally friendly units appeared on the market. Its excellent thermal insulation properties provide significant energy savings for heating in winter and air conditioning in summer. This reduces the load on the building structure and creates conditions for better earthquake protection with reduced amounts of concrete and reinforcement. They make up about 80% of the total.
The desire to build at any cost with the help of aerated concrete has begun to gain dimensions of building euphoria and is relatively new for our building material in the country, also in places not suitable for this purpose, and also without observing the technology of working with it. Effective Application every new material also requires new ones construction technologies, new bonding, primer and other materials, use of ready-made plasters and plaster, etc. That's why we will try to introduce you to some details in working with aerated concrete blocks.
- Brick walls and their minimum thickness
- Laying the first rows of a brick load-bearing wall
- Laying a wall with 1 brick
- Alternation methods for laying and size of seams
- Calculation of wall thickness taking into account thermal conductivity
- The influence of additives in masonry mortar on wall thickness
The construction of modern country and cottage buildings is subject to high requirements in terms of protection against heat loss. External ones must have excellent load-bearing capabilities. Calculation of the thickness of brick walls must be clearly coordinated with all the requirements for the construction process.
The aerated concrete blocks produced by the company quickly began to banish the until recently traditional heavy, expensive and inconvenient ceramic blocks, better known as brick fours. Factory sealed yellow polyethylene aerated concrete blocks can now be seen on almost all of the more typical structures in Bulgaria, as well as in most building material warehouses. These two indicators determine the maintenance of healthy environment in a residential area.
Something that's hard to say about brickwork. What is aerated concrete? Aerated concrete is lightweight concrete produced in an autoclave from sand, cement, lime, water and aluminum by heating with water vapor at a pressure of about 12 atmospheres. Characteristic feature This is due to its highly porous structure, which arises as a result of the release of hydrogen gas during chemical reaction between aluminum and other components. The important thing is that all ingredients do not contain substances harmful to health.
The thickness of brick walls depends on the strength characteristics of the materials used and the properties of the insulation materials used.
Making the appropriate calculation, taking into account the coordination of the thickness of the wall and its reliability with standard brick parameters, we can come to the conclusion that the wall should have a width of about 3 m. The misunderstanding is as follows: a brick with the property of thermal resistance will not provide high load-bearing capacity to the walls.
Brick walls and their minimum thickness
There are no universal materials on the construction market that meet all requirements in any area. For certain conditions, a certain wall thickness is suitable. The typical dimensions of the most common types of bricks are 250*120*65 mm, they are standard.
The thickness of the load-bearing brick wall is calculated, taking into account the standard brick parameters of 25 cm. The requirements for the choice of wall thickness are often determined by the loads on it, since the frame of any building is a system of load-bearing walls, which must be safe and reliable.
Load on load-bearing walls usually includes more than just their weight. It also includes the weight of other elements, which are partitions, ceilings, roofs, etc. The construction of buildings from materials requires additional reserves.
The minimum thickness of load-bearing brick walls should be less than 1 brick with a standard thickness of 25 cm, which is necessary to ensure normal heat-saving qualities.
Return to contents
Laying the first rows of a brick load-bearing wall
If the brickwork is made of the appropriate length, then the building will have a long service life. The required thickness of external load-bearing walls or internal ones is half a brick, or 12 cm.
To obtain an even masonry, it is necessary to prepare high-quality cement mortar. Composite external walls deserve special attention; they contain several different layers. These layers serve to ensure the safety of the structure, which is accompanied by conservation of thermal resistance. A combined external wall includes the presence of:
- heat insulators, which are foam plastic or mineral wool;
- materials, which are special panels, bricks for cladding, including plaster for the external decoration of the walls of the building.
The thickness of the walls is taken into account depending on factors related to temperature during the cold period, the type of heat insulator. The main function of thermal protection of walls belongs to the heat insulator, and its layer volume will change the thickness of the external wall. The masonry is kept to a minimum, but with the use of modern heat insulators, a high level of the result obtained is guaranteed. Certain types of bricks, lightweight concrete stones, and small-sized concrete blocks that have a solid structure or have vertical voids are used. The mass of these building materials is much greater than that of a simple brick. For example, their size is 88 mm, 140 mm or 188 mm, which ensures the connection of individual horizontally matching rows and seams with brick cladding.
If you use high-strength solid brick, then in terms of heat-shielding characteristics it is less convenient for masonry than multi-hole and thermal bricks. It has the greatest porosity, weighing from 1100 to 1300 kg/m³. They use grades of brick from M50 to M150, and grades of lime or cement mixtures, that is, binders, from 10 to 25. Masonry is carried out using special mixtures with a density of more than 1500 kg/m³. They are called cool mixtures and include cement-lime, sand, and light ones.
Solid masonry of solid brick walls with a width of more than 38 cm is not considered a way out. After all, a brick of these sizes, that is, its large mass, can make masonry less economical. This thickness of the outer wall, assigned according to thermal engineering calculations, can be considered excessive. Its load-bearing capacity is only 1/4 useful; for this reason, the construction of cottages is carried out on the basis of light types of brick. The use of appropriate heterogeneous wall masonry systems of layered or lightweight type involves the use of lightweight concrete stones.
Return to contents
Laying a wall with 1 brick
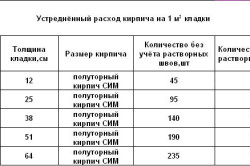
Average brick consumption per 1m2.
The thickness of a wall of 1 brick is equivalent to 25 cm. The bricks are laid side by side, but this does not affect the safety and strength of the wall. The main role in the quality of the masonry is played by the mortar used, which will not lead to jamming of the bricks. The minimum wall thickness, that is, 25 cm, is quite common. Depending on external influences and the load on the walls, the thickness is sometimes 1.5, 2 and 2.5 bricks.
The basic rule of masonry is the use of high-quality dressing of each vertical seam. The use of vertical joints must necessarily be accompanied by an overlap with the top row of bricks. By ligating, you can not only increase the strength of load-bearing walls, but also moderate the distribution of loads that arise.
There are various types dressings for seams: vertical; transverse, preventing the movement of brickwork, etc. For example, longitudinal ones do not allow the wall to delaminate vertically, which prevents movement of the horizontal type of masonry, and contribute to a moderate distribution of load along the load-bearing walls.
A wall of 1 brick is often laid according to the chosen system. For example, a single-row system involves laying the 1st row with the tongue side on the outside, and the next row is laid with the butt side of the brick outward. So, if the entire seam running across the masonry is displaced by 1/2 of a brick, then each longitudinal seam is displaced by 1/2 of a brick.
Return to contents
Alternation methods for laying and size of seams
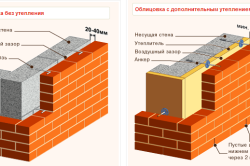
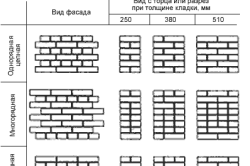
Options for masonry with cladding.
A number of alternation methods are used when laying. If a single brick is used, then usually choose ligation using the butt method, which is carried out after every 6th row. When using a thicker type of brick, the number of spoon rows is minimized to 5. This type of connection is due to the high strength of the structure, which contributes to a moderate distribution of the entire load.
The thickness of the walls is 1.5 bricks made by laying from the corners, and the laying of the 1st row must be done at right angles with bricks, the thickness of which is 38 cm. It is convenient to control the correctness of the laying of the rows with a construction corner.
The 1st row is laid using a cord stretched over the entire height between the 1st and 2nd bricks. The interlocking surface of the bricks is made facing the outer side of the wall, and the masonry of the 1st row is oriented towards the inner side and the interfacing part inward. Laying the next row is carried out in the reverse order. This is how a mirror type of reflection of the masonry may appear in the 1st row.
As a result, the inner side of the walls is laid in 1, and the outer side in half a brick. Masonry of 1.5 is widely used, which occurs due to the reliability of the walls due to their high strength. The vertical seams do not coincide; they are overlapped by a solid part of the next row of masonry.
If an increase in the size of the seams is associated with the appearance of a deviation from the vertical plane or from the chosen direction of the masonry, then its method also changes. When constructing structures in areas characterized by severe frosts, the use of thermal insulators will make it possible to create a load-bearing wall of 2 bricks, which will be the most suitable option.
Return to contents
Calculation of wall thickness taking into account thermal conductivity
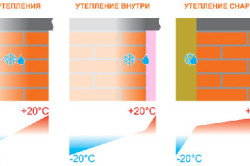
The thickness of the walls is often indicated in the construction plan; it is calculated taking into account all the reasons that influence the operation of the building in the future. The wall thickness should be calculated for the entire building. The purpose of the calculation is to develop a durable and comfortable structure. When calculating wall thickness, a special formula for determining thermal conductivity is used, which is written as R = S/k, where:
- S – material thickness, m;
- k – thermal conductivity coefficient;
- R is the thermal resistance of the walls of buildings erected in a certain region.
The value of the coefficient k depends on the region of future development. For example, k is equal to 3-3.2 for the Leningrad and Moscow regions, and for Yakutia and neighboring regions, which are republics of the Far North, k = 4.89.
Any building material has a thermal conductivity index. The thermal conductivity of a single brick is 0.58 W/m°C, which meets the standards. The thickness of the walls cannot be less than 250 mm including the heat insulator. Taking into account the thermal conductivity of bricks will help in the future to avoid excessive energy costs for heating the premises of the building.

The method, which involves continuous masonry during construction, is economical even if there is external or internal insulation. Thickness external walls depends on the strength requirements for the structure.
If there is an internal layer of insulation, it is necessary to prevent the occurrence of condensation. This will require a vapor barrier. If there are external layers of thermal insulation, plastering of the surface will be required.
The greatest load requires reinforcement of partitions, piers and support pillars using an iron wire network with a diameter of 3-6 mm in height every 3 or 5 rows. Partitions are usually laid out in half-bricks 12 cm wide. The cross-sectional dimensions of the pillars should be 25 cm by 38 cm or more. Sometimes the thickness of the partitions can be 6.5 cm, and the method is called “brick on edge”. If the length of the partitions is more than 1.5 m, which are made using this method, the structure of the partitions should be reinforced with rods every 2 rows.
The brick surface of the walls is characterized by the greatest thermal inertia, which requires a sufficient amount of time for the wall to fully warm up. With a minimum thickness of a brick wall, its mass is greatest, and the process of cooling or warming up the wall will be long. Thanks to these properties of the brick, the temperature level in the room will be constant throughout the day, which is a fundamental advantage. High level The thermal inertia of walls is often not favorable.
For example, in the cool season, operating country houses is a problematic task due to dampness in them. If the walls are frozen in winter, then this requires basic and additional heating, and temperature changes in the building are associated with the formation of condensation. For this reason, the minimum wall thickness requires additional cladding using boards.
 B1 in English what level?
B1 in English what level? Managing verbs in German - German online - Start Deutsch
Managing verbs in German - German online - Start Deutsch Conjugation of the verb haben (to have) in the present tense
Conjugation of the verb haben (to have) in the present tense